- Minimum Number of Operations to Sort a Binary Tree by Level
- Hash Map
- Bit Manipulation
- Cycle Sort
- Bit Manipulation + Cycle Sort
Minimum Number of Operations to Sort a Binary Tree by Level
You are given the root of a binary tree with unique values.
In one operation, you can choose any two nodes at the same level and swap their values.
Return the minimum number of operations needed to make the values at each level sorted in a strictly increasing order.
The level of a node is the number of edges along the path between it and the root node.
Example 1:
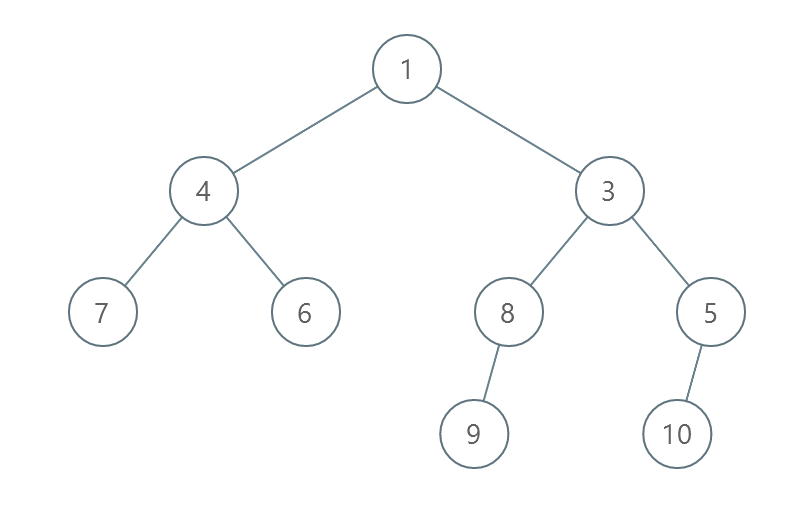
Input: root = [1,4,3,7,6,8,5,null,null,null,null,9,null,10]
Output: 3
Explanation:
- Swap 4 and 3. The 2nd level becomes [3,4].
- Swap 7 and 5. The 3rd level becomes [5,6,8,7].
- Swap 8 and 7. The 3rd level becomes [5,6,7,8].
We used 3 operations so return 3.
It can be proven that 3 is the minimum number of operations needed.
Example 2:
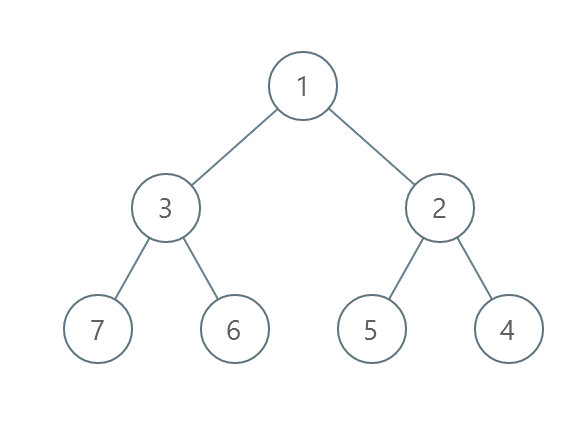
Input: root = [1,3,2,7,6,5,4]
Output: 3
Explanation:
- Swap 3 and 2. The 2nd level becomes [2,3].
- Swap 7 and 4. The 3rd level becomes [4,6,5,7].
- Swap 6 and 5. The 3rd level becomes [4,5,6,7].
We used 3 operations so return 3.
It can be proven that 3 is the minimum number of operations needed.
Example 3:
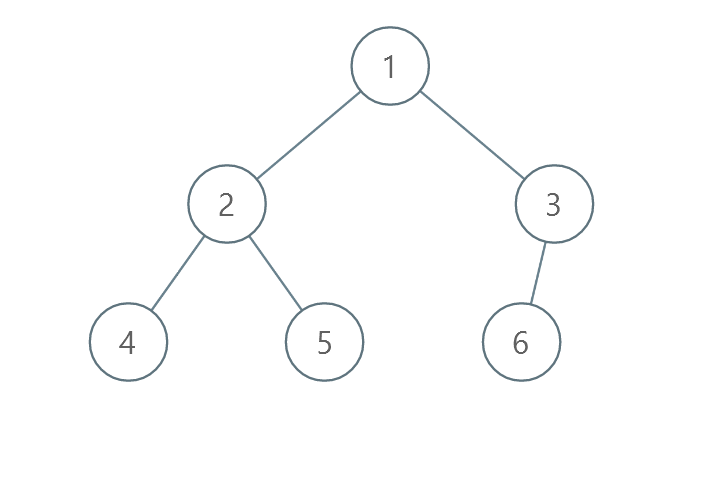
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: 0
Explanation: Each level is already sorted in increasing order so return 0.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, \(10^5\)].
- 1 <= Node.val <= \(10^5\)
- All the values of the tree are unique.
Hash Map
class Solution {
fun minimumOperations(root: TreeNode?): Int {
if (root == null) return 0
var operators = 0
val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>()
queue.offer(root)
while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
val size = queue.size
val list = MutableList(size) { 0 }
repeat(size) {
val node = queue.pop()
list[it] = node.`val`
node.left?.apply(queue::offer)
node.right?.apply(queue::offer)
}
operators += minSwaps(list)
}
return operators
}
fun minSwaps(original: MutableList<Int>): Int {
var swaps = 0
val target = original.sorted()
val value2Index = original.withIndex().associate { Pair(it.value, it.index) }.toMutableMap()
repeat(original.size) { i ->
if (original[i] != target[i]) {
swaps++
val index = value2Index[target[i]]!!
value2Index[original[i]] = index
original[index] = original[i]
}
}
return swaps
}
}
Bit Manipulation
class Solution {
val shift = 20
val mask = 1L.shl(shift) - 1
fun minimumOperations(root: TreeNode?): Int {
if (root == null) return 0
var operators = 0
val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>()
queue.offer(root)
while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
val size = queue.size
val list = MutableList(size) { 0L }
repeat(size) {
val node = queue.pop()
list[it] = node.`val`.toLong().shl(shift) + it
node.left?.apply(queue::offer)
node.right?.apply(queue::offer)
}
list.sort()
var i = 0
while (i < list.size) {
val index = list[i].and(mask).toInt()
if (index != i) {
list[i] = list[index].also { list[index] = list[i] }
operators++
} else i++
}
}
return operators
}
}
Cycle Sort
class Solution {
fun minimumOperations(root: TreeNode?): Int {
if (root == null) return 0
var operators = 0
val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>()
queue.offer(root)
while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
val size = queue.size
val list = MutableList(size) { 0 }
repeat(size) {
val node = queue.pop()
list[it] = node.`val`
node.left?.apply(queue::offer)
node.right?.apply(queue::offer)
}
operators += cycleSort(list)
}
return operators
}
fun cycleSort(list: MutableList<Int>): Int {
val value2Index = list.withIndex().associate { Pair(it.value, it.index) }
list.sort()
val visited = BooleanArray(list.size) { false }
var ans = 0
repeat(list.size) { i ->
if (visited[i] || value2Index[list[i]] == i) return@repeat
var j = i
var cycleSize = 0
while (!visited[j]) {
visited[j] = true
j = value2Index[list[j]]!!
cycleSize++
}
ans += cycleSize - 1
}
return ans
}
}
Bit Manipulation + Cycle Sort
class Solution {
val shift = 20
val mask = 1L.shl(shift) - 1
fun minimumOperations(root: TreeNode?): Int {
if (root == null) return 0
var operators = 0
val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>()
queue.offer(root)
while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
val size = queue.size
val list = MutableList(size) { 0L }
repeat(size) {
val node = queue.pop()
list[it] = node.`val`.toLong().shl(shift) + it
node.left?.apply(queue::offer)
node.right?.apply(queue::offer)
}
operators += cycleSort(list)
}
return operators
}
fun cycleSort(list: MutableList<Long>): Int {
list.sort()
val visited = BooleanArray(list.size) { false }
var ans = 0
repeat(list.size) { i ->
if (visited[i] || list[i].and(mask).toInt() == i) return@repeat
var j = i
var cycleSize = 0
while (!visited[j]) {
visited[j] = true
j = list[j].and(mask).toInt()
cycleSize++
}
ans += cycleSize - 1
}
return ans
}
}